Abstract
Case Presentation
A case of coexistent acute severe alcoholic and Q fever hepatitis: The useful contribution of repeated liver biopsies
Lucia Zampaglione, Aurélie Bornand, Nicolas Goossens, Lucas Ramer, Giulia Magini, Marie Ongaro, Andreas Cerny, Laura Rubbia-Brandt, Jean-Louis Frossard and Laurent Spahr*
Published: 23 September, 2022 | Volume 6 - Issue 1 | Pages: 034-038
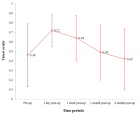
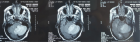
Acute Q fever is a worldwide zoonotic infection due to C. burnetii that may be associated with hepatitis. Nonspecific clinical and biological manifestations may accompany liver involvement, including hepatomegaly and elevated liver biological tests. However, the presence of jaundice is rare. Therefore, making a diagnosis of Q fever hepatitis may be difficult in an afebrile patient with jaundice of recent onset, altered liver function tests, excessive alcohol intake and no reported contact with animals. We report here the diagnostic work-up and complex clinical management of a patient presenting with acute hepatitis resulting from both C. burnetii infection and severe alcoholic steatohepatitis. Positive serology together with a detailed examination of the liver biopsy was able to reveal the coexistence of both Q fever hepatitis with typical fibrin-ring granulomas as well as florid lesions of alcoholic steatohepatitis. A combination of antibiotics, hydroxychloroquine and steroids, guided by the helpful description of changes in histological alterations on repeated liver biopsies during the course of the disease contributed to the slow but favorable outcome.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001036 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Alcoholic steatohepatitis; Q fever hepatitis; Coxiella burnetii; Fibrin-ring granuloma; Liver biopsy
References
- Parker NR, Barralet JH, Bell AM. Q fever. Lancet. 2006 Feb 25;367(9511):679-88. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68266-4. PMID: 16503466.
- Geha R, Peters M, Gill RM, Dhaliwal G. Histology Rings True. N Engl J Med. 2017 Mar 2;376(9):869-874. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcps1609391. PMID: 28249146.
- Ali S, Prakash S, Murali AR. Hepatic Manifestations of Nonhepatotropic Infectious Agents Including Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2, Adenovirus, Herpes Simplex Virus, and Coxiella burnetii. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2021 Jun;50(2):383-402. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2021.02.012. Epub 2021 Apr 23. PMID: 34024447.
- Choi HC, Lee SH, Kim J, Kim SH, Hwang JH, Kim JW, Jeong SH, Kim H. A case of acute q Fever with severe acute cholestatic hepatitis. Gut Liver. 2009 Jun;3(2):141-4. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2009.3.2.141. Epub 2009 Jun 30. PMID: 20431739; PMCID: PMC2852695.
- Keijmel SP, Krijger E, Delsing CE, Sprong T, Nabuurs-Franssen MH, Bleeker-Rovers CP. Differentiation of Acute Q Fever from Other Infections in Patients Presenting to Hospitals, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015 Aug;21(8):1348-56. doi: 10.3201/eid2108.140196. PMID: 26196955; PMCID: PMC4517711.
- Vanden Bussche S, Smets K, Steelandt T, Van Eyken P, Caenepeel P, Robaeys G. A case of Q fever with hepatitis and an atypical skin lesion. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2018 Jul-Sep;81(3):441-442. PMID: 30350538.
- Lee M, Jang JJ, Kim YS, Lee SO, Choi SH, Kim SH, Yu E. Clinicopathologic features of q Fever patients with acute hepatitis. Korean J Pathol. 2012 Feb;46(1):10-4. doi: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.10. Epub 2012 Feb 23. PMID: 23109972; PMCID: PMC3479695.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: [email protected]; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of alcohol-related liver disease. J Hepatol. 2018 Jul;69(1):154-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.018. Epub 2018 Apr 5. PMID: 29628280.
- Ramond MJ, Poynard T, Rueff B, Mathurin P, Théodore C, Chaput JC, Benhamou JP. A randomized trial of prednisolone in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Feb 20;326(8):507-12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199202203260802. PMID: 1531090.
- Spahr L, Lanthier N, Tihy M, Frossard JL, Rubbia-Brandt L, Goossens N. Clinical Presentation and Gene Expression of Acute Alcohol-Induced Microvesicular Steatosis Mimicking Alcoholic Hepatitis. Hepatol Commun. 2021 Jan 9;5(4):618-628. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1669. PMID: 33860120; PMCID: PMC8034579.
- Gustot T, Felleiter P, Pickkers P, Sakr Y, Rello J, Velissaris D, Pierrakos C, Taccone FS, Sevcik P, Moreno C, Vincent JL; EPIC II Group of Investigators. Impact of infection on the prognosis of critically ill cirrhotic patients: results from a large worldwide study. Liver Int. 2014 Nov;34(10):1496-503. doi: 10.1111/liv.12520. Epub 2014 Mar 26. PMID: 24606193.
- Dauby N, Gomez Galdon M, Montesinos I, Van Esbroeck M, Sersté T. Q-fever associated granulomatous hepatitis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Jun;95:113-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.002. Epub 2020 Apr 10. PMID: 32283284.
- Aguilar-Olivos N, del Carmen Manzano-Robleda M, Gutiérrez-Grobe Y, Chablé-Montero F, Albores-Saavedra J, López-Méndez E. Granulomatous hepatitis caused by Q fever: a differential diagnosis of fever of unknown origin. Ann Hepatol. 2013 Jan-Feb;12(1):138-41. PMID: 23293205.
- Travis LB, Travis WD, Li CY, Pierre RV. Q fever. A clinicopathologic study of five cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Nov;110(11):1017-20. PMID: 3778120.
- Louvet A, Naveau S, Abdelnour M, Ramond MJ, Diaz E, Fartoux L, Dharancy S, Texier F, Hollebecque A, Serfaty L, Boleslawski E, Deltenre P, Canva V, Pruvot FR, Mathurin P. The Lille model: a new tool for therapeutic strategy in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids. Hepatology. 2007 Jun;45(6):1348-54. doi: 10.1002/hep.21607. PMID: 17518367.
- Louvet A, Labreuche J, Artru F, Bouthors A, Saffers P, Rolland B, Dharancy S, Lassailly G, Canva-Delcambre V, Duhamel A: Drivers of short- and long-term mortality in severe alcoholic hepatitis: a complex relationship between alcohol relapse and early improvement in liver function. Hepatology 2016 ; 64:22a-22a.
- Dupuis G, Petite J, Péter O, Vouilloz M. An important outbreak of human Q fever in a Swiss Alpine valley. Int J Epidemiol. 1987 Jun;16(2):282-7. doi: 10.1093/ije/16.2.282. PMID: 3301708.
- Finn T, Babushkin F, Geller K, Alexander H, Paikin S, Lellouche J, Atiya-Nasagi Y, Cohen R. Epidemiological, clinical and laboratory features of acute Q fever in a cohort of hospitalized patients in a regional hospital, Israel, 2012-2018. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jul 15;15(7):e0009573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009573. PMID: 34264953; PMCID: PMC8315502.
- Raoult D. Host factors in the severity of Q fever. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:33-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42204.x. PMID: 2198833.
- Crespo M, Sopeña B, Bordón J, de la Fuente J, Rubianes M, Martinez-Vázquez C. Steroids treatment of granulomatous hepatitis complicating Coxiella burnetii acute infection. Infection. 1999 Mar-Apr;27(2):132-3. doi: 10.1007/BF02560514. PMID: 10219646.
- Altamirano J, Miquel R, Katoonizadeh A, Abraldes JG, Duarte-Rojo A, Louvet A, Augustin S, Mookerjee RP, Michelena J, Smyrk TC, Buob D, Leteurtre E, Rincón D, Ruiz P, García-Pagán JC, Guerrero-Marquez C, Jones PD, Barritt AS 4th, Arroyo V, Bruguera M, Bañares R, Ginès P, Caballería J, Roskams T, Nevens F, Jalan R, Mathurin P, Shah VH, Bataller R. A histologic scoring system for prognosis of patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2014 May;146(5):1231-9.e1-6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.01.018. Epub 2014 Jan 15. PMID: 24440674; PMCID: PMC3992184.
Figures:
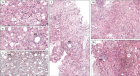
Figure 1
Figure 2
Similar Articles
-
A case of coexistent acute severe alcoholic and Q fever hepatitis: The useful contribution of repeated liver biopsiesLucia Zampaglione,Aurélie Bornand,Nicolas Goossens,Lucas Ramer,Giulia Magini,Marie Ongaro,Andreas Cerny,Laura Rubbia-Brandt,Jean-Louis Frossard,Laurent Spahr*. A case of coexistent acute severe alcoholic and Q fever hepatitis: The useful contribution of repeated liver biopsies. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001036; 6: 034-038
Recently Viewed
-
Agriculture High-Quality Development and NutritionZhongsheng Guo*. Agriculture High-Quality Development and Nutrition. Arch Food Nutr Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.afns.1001060; 8: 038-040
-
A Low-cost High-throughput Targeted Sequencing for the Accurate Detection of Respiratory Tract PathogenChangyan Ju, Chengbosen Zhou, Zhezhi Deng, Jingwei Gao, Weizhao Jiang, Hanbing Zeng, Haiwei Huang, Yongxiang Duan, David X Deng*. A Low-cost High-throughput Targeted Sequencing for the Accurate Detection of Respiratory Tract Pathogen. Int J Clin Virol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001056; 8: 001-007
-
A Comparative Study of Metoprolol and Amlodipine on Mortality, Disability and Complication in Acute StrokeJayantee Kalita*,Dhiraj Kumar,Nagendra B Gutti,Sandeep K Gupta,Anadi Mishra,Vivek Singh. A Comparative Study of Metoprolol and Amlodipine on Mortality, Disability and Complication in Acute Stroke. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001108; 9: 039-045
-
Development of qualitative GC MS method for simultaneous identification of PM-CCM a modified illicit drugs preparation and its modern-day application in drug-facilitated crimesBhagat Singh*,Satish R Nailkar,Chetansen A Bhadkambekar,Suneel Prajapati,Sukhminder Kaur. Development of qualitative GC MS method for simultaneous identification of PM-CCM a modified illicit drugs preparation and its modern-day application in drug-facilitated crimes. J Forensic Sci Res. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001043; 7: 004-010
-
A Gateway to Metal Resistance: Bacterial Response to Heavy Metal Toxicity in the Biological EnvironmentLoai Aljerf*,Nuha AlMasri. A Gateway to Metal Resistance: Bacterial Response to Heavy Metal Toxicity in the Biological Environment. Ann Adv Chem. 2018: doi: 10.29328/journal.aac.1001012; 2: 032-044
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."